Insurance DenialFlow Case Study Web Modernization AI Denial Resolution Assistant
Insurance DenialFlow Case Study
70% cost reduction
Web-first access
AI-assisted appeals
Release in sprints
*Where metrics are “reported,” they reflect client-side operational outcomes shared during the engagement. Replace with audited production numbers for a final public version if needed.
Primary Objective
Create a single digital window to invite, onboard, credential, and verify medical staff—with compliance controls, eSignature, tasking, and reporting built in.
Client
Anonymized (Hospital / HealthTech startup)
Users:
Admin, HR, Employees, Prospective Employees
Region:
USA
Timeline:
45 Days (MVP)
Stack:
React + Vite + TypeScript, Node.js, Postgres, AWS EC2
Executive Summary
Hospital staff onboarding is rarely a “form-fill” exercise. It’s a compliance-heavy process involving personal and professional history, credentials, licenses, medical checks, background documentation, approvals, and signatures. In a paper-driven workflow, every handoff introduces delay and risk.
What changed
- From paper packets to an 11-step onboarding flow with validations and structured review.
- From scattered documents to a centralized repository on Amazon S3, with access controls and versioning patterns.
- From manual approvals to task-based routing and location-specific compliance requirements.
- From weak traceability to audit logs capturing who changed what, when, and why.
The Challenge
The existing denial platform was desktop-based—creating device dependency, installation overhead, inconsistent user experience, and data sync problems. As claim volume and stakeholders grew, the system became operationally expensive to maintain and difficult to scale.
Operational pain
- Limited access: Users needed specific machines/OS environments to operate reliably.
- Workflow delays: Installing updates and troubleshooting compatibility slowed teams down.
- UI inconsistencies: Different setups led to inconsistent behavior and higher support overhead.
- Error-prone tracking: Manual handoffs increased the chance of missed appeals and stale statuses.
Technical pain
- Performance variability: Local installs + device constraints created uneven performance.
- Upgrade friction: Distributing and maintaining desktop builds increased cycle time.
- Scalability constraints: Hard to support more users, analytics, and near-real-time dashboards.
- Modern AI workflows: Desktop foundation made it harder to introduce AI-driven resolution assistance.
Goals & Success Criteria
We aligned on a web-first platform that is easy to access, simpler to maintain, and built for secure scale—while modernizing the denial workflow with AI-assisted recommendations.
Business goals
- Digitize denial workflows into an accessible web portal.
- Create a consistent UI/UX that reduces errors and training time.
- Accelerate appeals preparation using contextual AI assistance.
- Reduce installation, maintenance, and rework costs.
Technical goals
- Design for scalability, availability, and maintainability.
- Implement secure authentication and role-based authorization.
- Improve performance via caching and efficient data access patterns.
- Enable multi-model LLM integration with governance controls.
Solution Overview
We rebuilt DenialFlow as a modern web platform with a React/TypeScript frontend, Node.js backend services, MSSQL as the system of record, and Redis for caching. A dedicated AI assistant layer integrates with multiple LLM providers while enforcing security boundaries and operational controls.
High-level Architecture
Users (Admin / Analyst / Viewer / Insurance Agent)
│ (JWT / OAuth2 + Role-based access)
▼
React + Vite + TypeScript UI
(TanStack Query/Table, filters, exports, charts)
│
▼
Node.js API (REST)
- Claims & Denials services
- Workbench workflows
- User & role management
- AI orchestration layer
│
├── MSSQL (Prisma ORM)
│ - Claims, denials, codes, status history
│ - Workbench queues, assignments
│ - Audit events (who did what & when)
│
├── Redis cache
│ - hot lists, filters, lookup tables
│ - rate limiting & session helpers (optional)
│
├── AI Providers (configurable)
│ - OpenAI / Gemini / Anthropic
│ - model + token + safety settings via Admin Settings
│
└── AWS Services
- Hosting + networking
- Email via Amazon SES
- Monitoring/alerts + log aggregation (dashboards)
This diagram represents the implemented design intent and system boundaries based on provided project details. If you want, I can also provide a Mermaid diagram version for documentation.
Product Modules Delivered
DenialFlow was designed around how real denial teams work: quick triage, deep investigation, structured appeal actions, governance, and visibility. Each module is optimized for high-volume workflows.
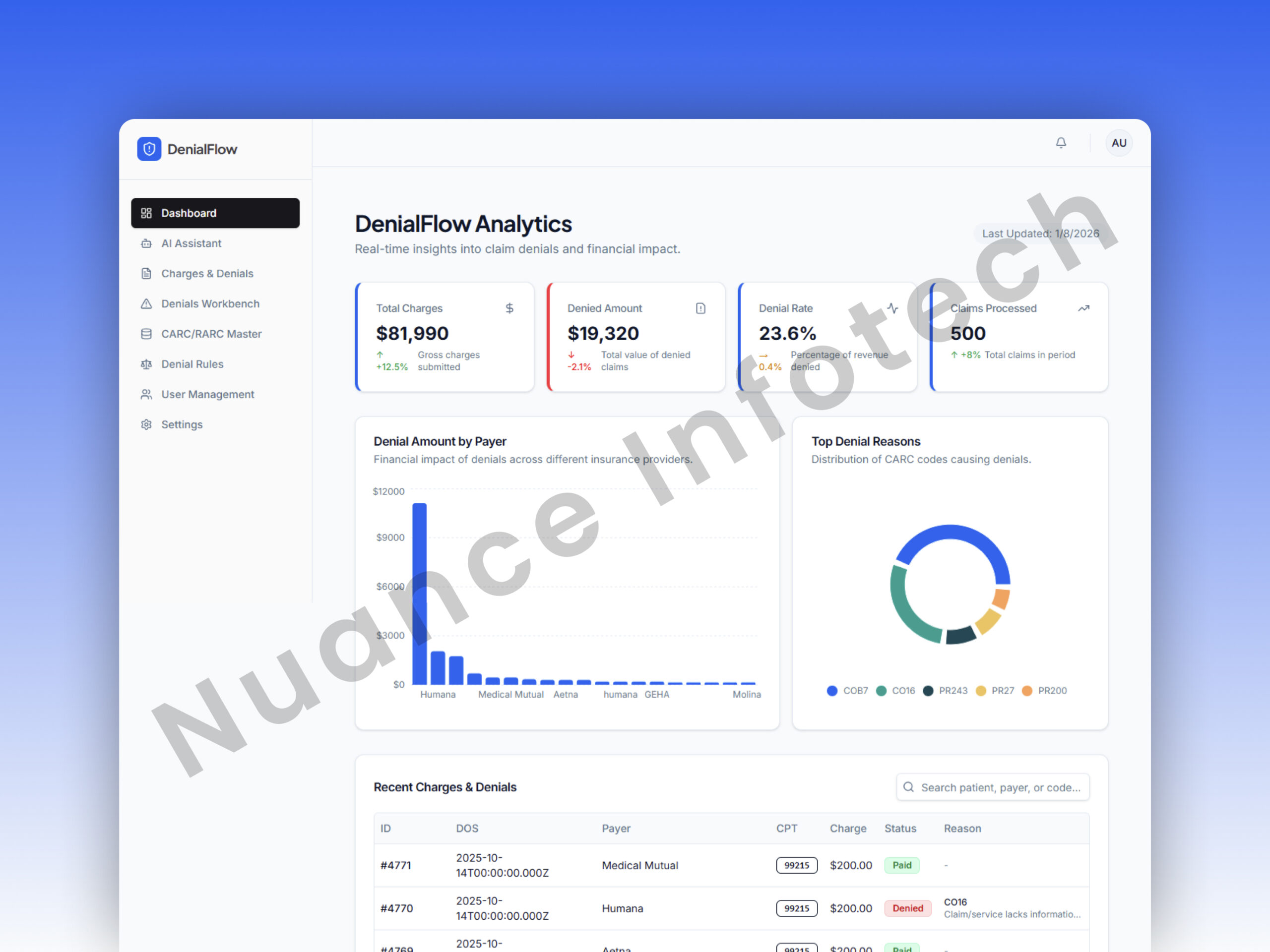
Dashboard
A real-time operational overview: recent denials, trend charts, interactive metrics, and quick entry points into the workbench—built to reduce time-to-action and improve throughput.
- Charts for denial categories and status movement
- “Recent Denials” activity feed for fast triage
- Role-aware widgets (analyst vs admin)
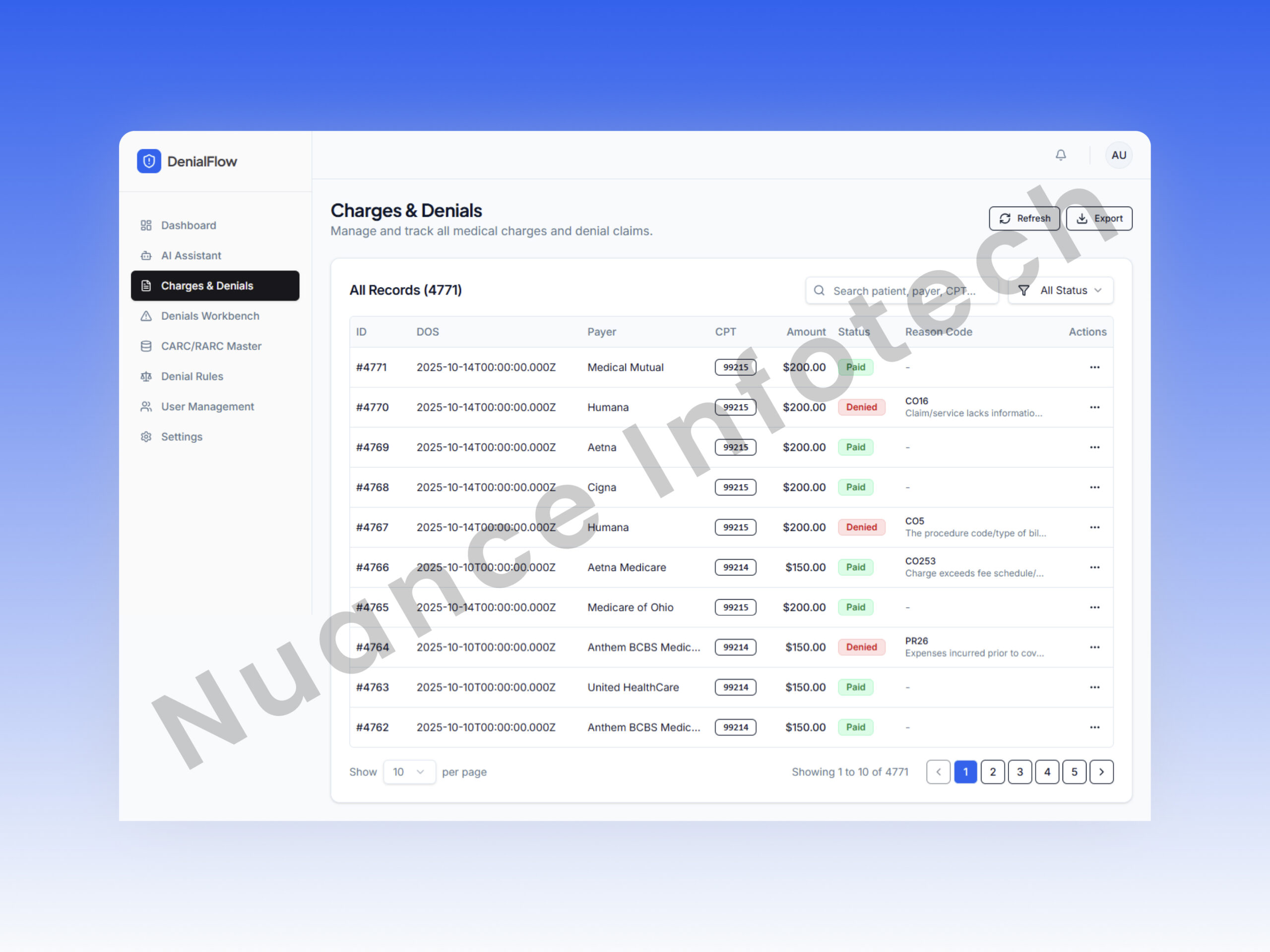
Claims & Denials
A unified list and detail view for claims lifecycle management: status, edits, resubmission/appeals workflows, and AI recommendations embedded directly inside the case context.
- Fast search + pagination + column filters
- Detail view with denial context and history
- Appeal edit + resubmit flows
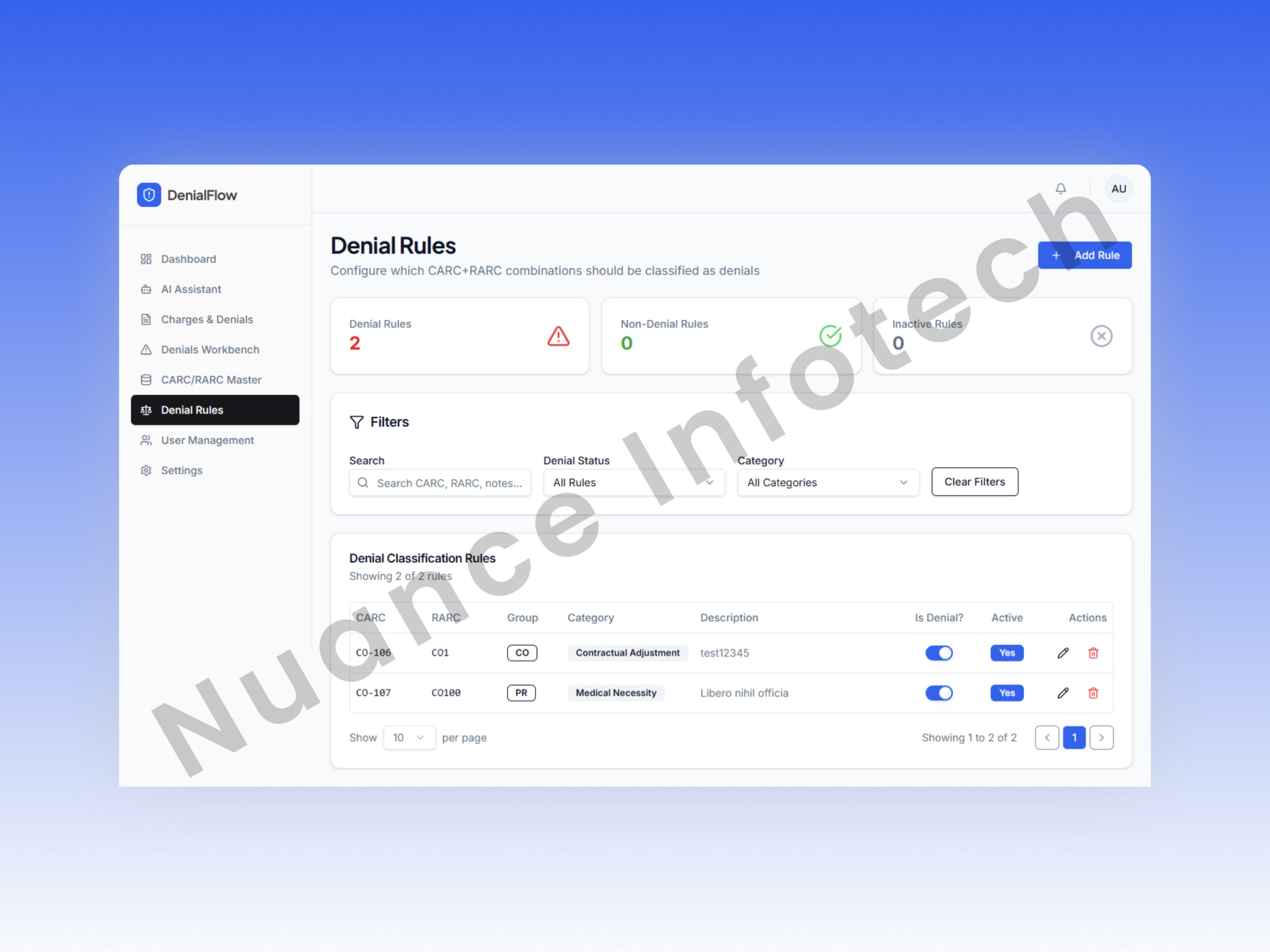
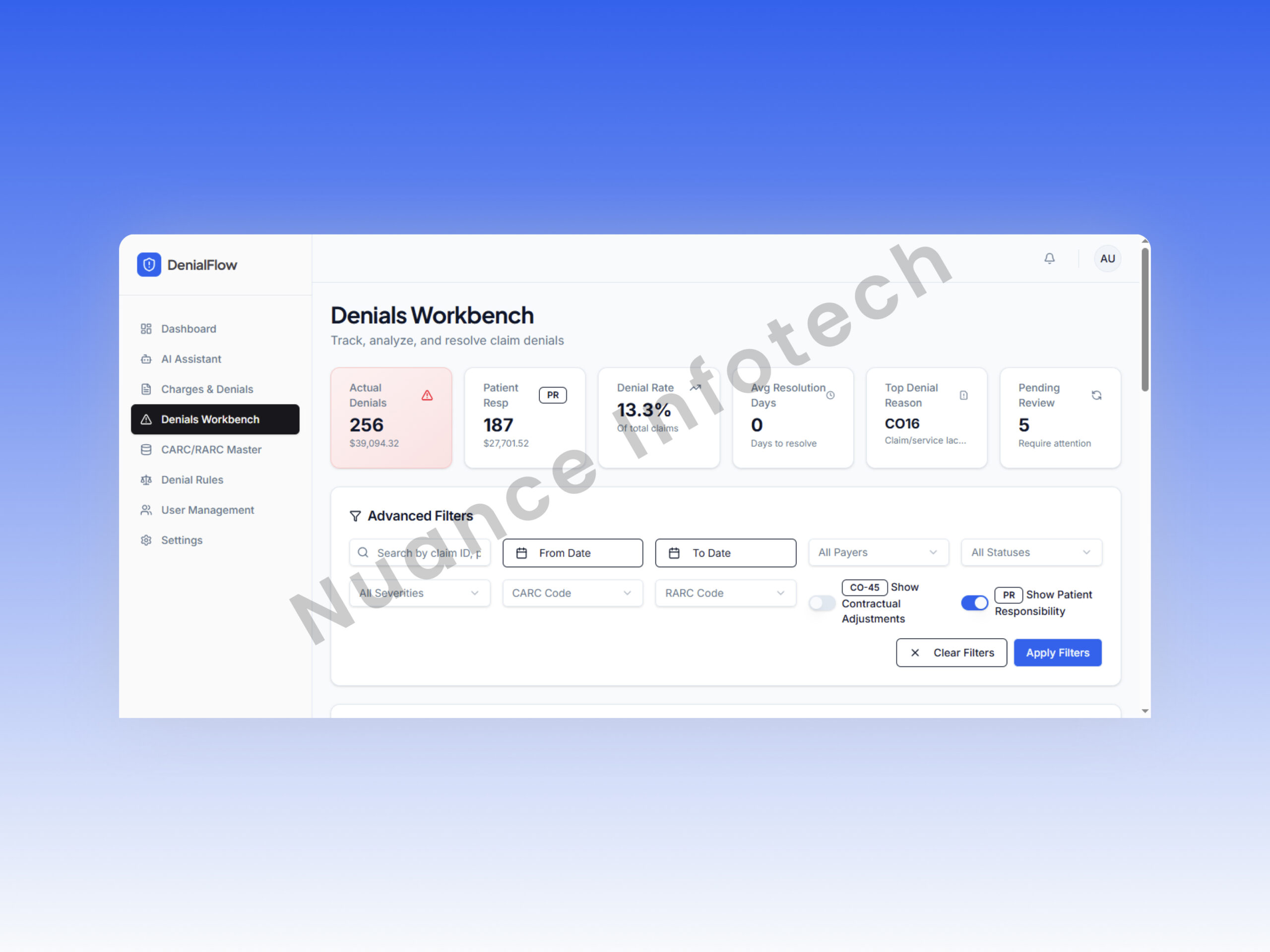
Denial Workbench
The operational hub: a queue-based workbench showing failed claims enriched with CARC/RARC + ICD context, advanced filters, export, and KPI summaries—so analysts can resolve more denials with fewer clicks.
- Advanced filters (payer, date, facility, code, status)
- Top KPI strip (volume, aging, resolution rate targets)
- Export-ready reporting for audits and reviews
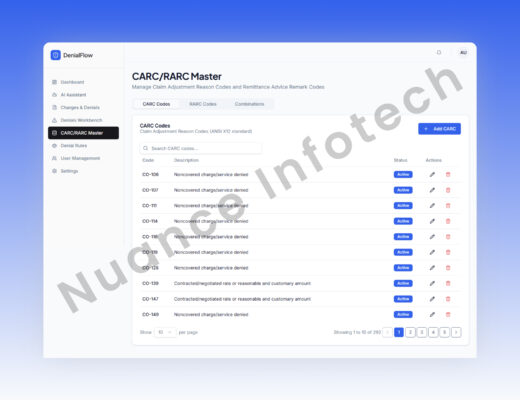
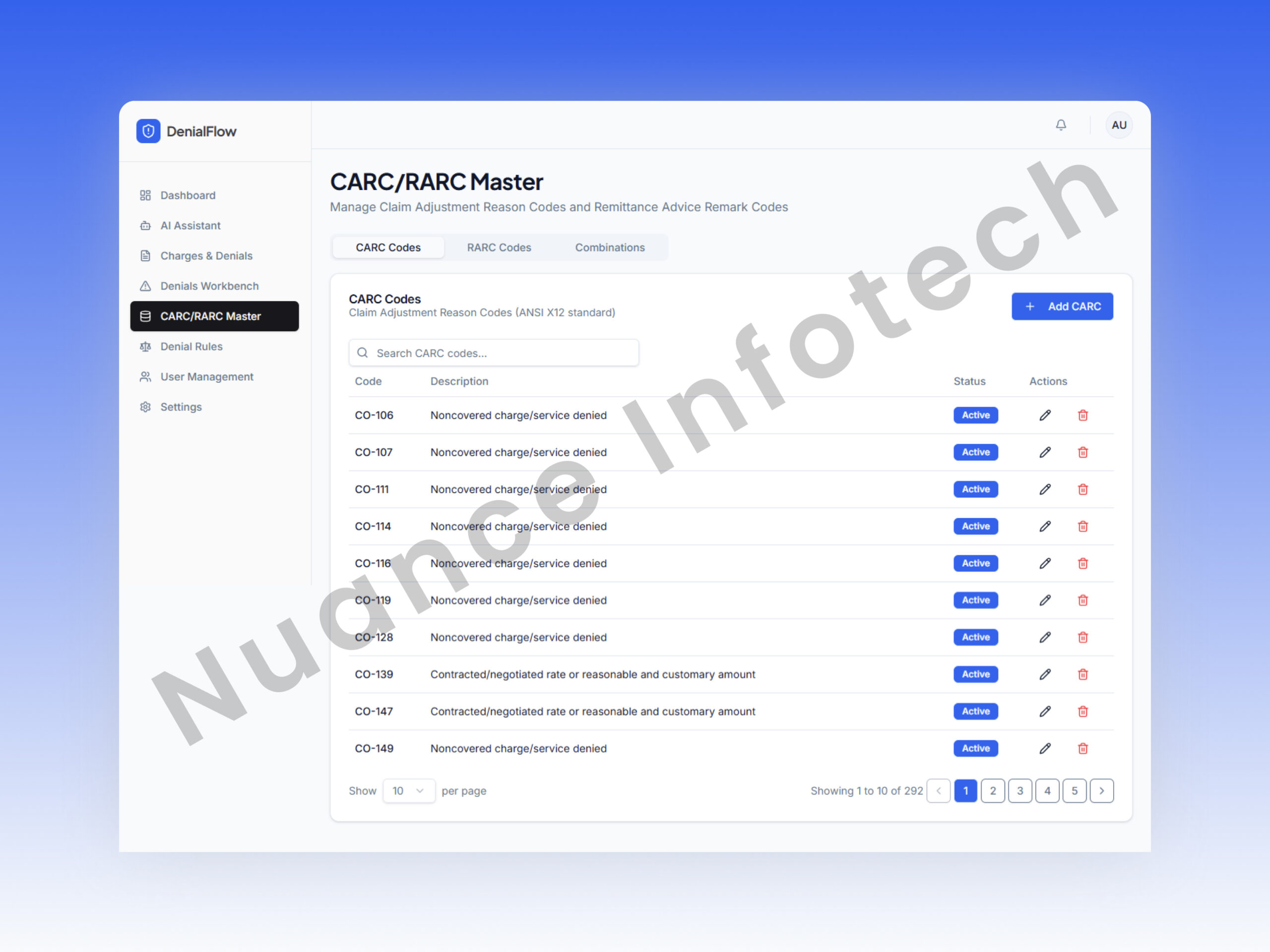
CARC / RARC Master
A governed master data module for denial reason codes that standardizes interpretation across teams and improves consistency of resolution decisions.
- Centralized code definitions & metadata
- Search + maintenance workflows
- Supports AI grounding inputs (see AI section)
User Management
Settings & Governance
A control plane for security preferences, notifications, and LLM integration—so the system remains adaptable without requiring a redeploy for provider/model changes.
- LLM provider + model + token management
- Notification preferences and platform policies
- Security feature toggles (org-specific)
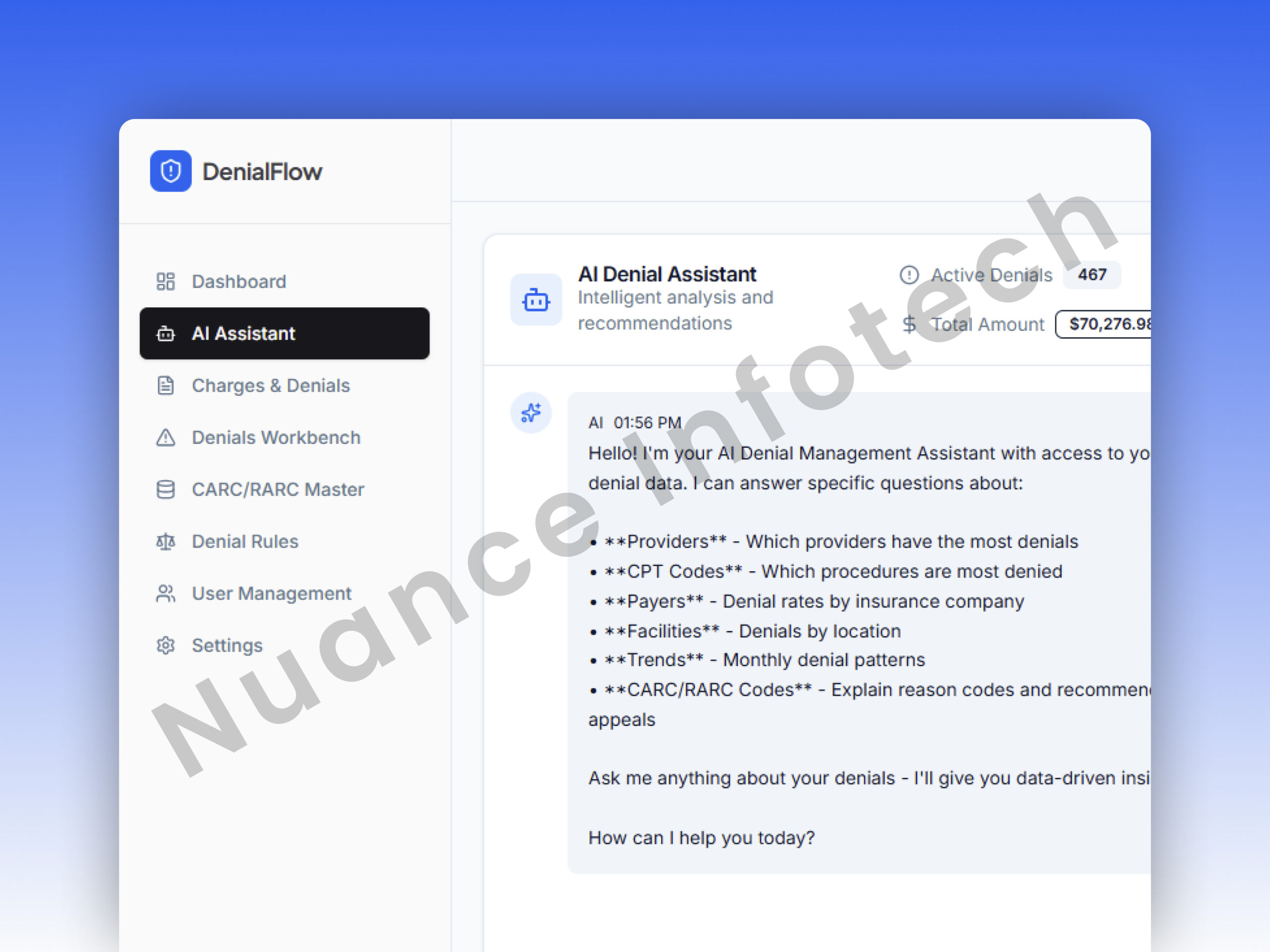
AI Denial Resolution Assistant
Denials are rarely “one-size-fits-all.” The assistant was built to be contextual: it uses claim details, denial codes (CARC/RARC), historical patterns, and payer-specific rules to generate actionable recommendations for analysts—without breaking governance controls.
What the assistant does
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Explains denials | Summarizes likely denial causes mapped to CARC/RARC and claim context. |
| Recommends fixes | Suggests missing fields, documentation, coding alignment, or resubmission changes. |
| Drafts appeal guidance | Generates appeal notes and improvement checklist per case. |
| Chat-based workflow | Analysts can ask follow-ups and refine resolution steps. |
| Multi-provider | Supports OpenAI, Gemini, Anthropic based on org preference. |
How we designed it safely
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Data minimization | Only required denial fields are shared for reasoning; sensitive fields can be masked. |
| Provider governance | LLM settings live in admin panel (model/token/rules), reducing engineering dependency. |
| Prompt structure | Strict templates enforce consistent outputs (cause → evidence → recommended action). |
| Audit logging | Track who requested AI output and what input context was used (without storing raw PHI when avoidable). |
| Fallback mode | If AI is disabled, workflows still function with deterministic rules and master code guidance. |
If your org handles PHI, we recommend HIPAA-aligned controls: redaction, provider DPAs/BAAs where applicable, and a formal data classification policy for prompts and logs.
Security, Privacy & Performance Engineering
Security & access control
- Authentication: OAuth2 + JWT session model (web-friendly, stateless tokens).
- Authorization: Role matrix enforced at API endpoints and UI route guards.
- Encryption: TLS in transit + encryption at rest for databases and secrets.
- Audit readiness: Track privileged actions (user changes, role updates, exports).
- Least privilege: Separate permissions for exports, approvals, and configuration changes.
Performance & scalability
- Redis caching: Hot datasets (lookup codes, recent queues) cached for faster dashboards.
- Query efficiency: Prisma + indexed MSSQL queries for filter-heavy workbench screens.
- Front-end optimization: TanStack Query caching + table virtualization for large lists.
- Exports: Background processing patterns recommended for large exports (to avoid UI blocking).
- Observability: Dashboards + alerting for API errors, latency, and queue health.
Delivery Process
Engineering workflow
- Sprint planning aligned to modules (Dashboard → Workbench → AI → Admin).
- Weekly demos for stakeholder validation and fast iteration.
- Dev / Stage / Prod environments with controlled releases.
- Incremental rollout to reduce change risk and gather feedback.
Quality assurance
- E2E testing: Playwright flows for login, denial workflows, filters, and exports.
- Regression suite: Feature-by-feature releases with repeatable test coverage.
- AI validation: Prompt tests to ensure output format consistency and avoid unsafe leakage.
- Performance checks: Load-aware testing on workbench filters and dashboard queries.
Outcomes & Business Impact
Measured / reported outcomes
- 70% cost reduction: Reduced multi-vendor dependency and rework cycles (reported).
- Installation time eliminated: Web access removed desktop setup and compatibility barriers.
- Higher stability: Sprint-based releases with strong E2E coverage reduced regression issues.
- Faster resolution: AI guidance shortened investigation-to-action time on common denial patterns.
Client feedback (representative)
“The web migration removed constant installation hurdles and made the system accessible across teams instantly. The denial workbench and AI recommendations helped our analysts resolve cases faster with more confidence, and releases were stable and predictable.”
*Testimonial written in anonymized form based on engagement outcomes shared by stakeholders.
Lessons Learned & Best Practices
1) Desktop-to-web migrations succeed when “workflow parity” comes first
- We prioritized replicating core denial workflows before introducing new capability.
- Once parity was reached, we improved the UX with workbench filters, faster navigation, and dashboard visibility.
- Adoption improved because users didn’t have to “relearn the job”—only the interface.
2) AI needs governance, not just an API key
- Provider/model switching in Admin Settings reduced operational dependency on engineering.
- Prompt templates created consistent outputs (cause → evidence → action) for analyst trust.
- We recommended PHI minimization and redaction policies when integrating LLMs into regulated workflows.
3) Performance comes from “data shape” + caching
- Workbench screens fail at scale without strong indexing and query planning.
- Redis caching reduced repeated lookups (CARC/RARC masters, hot queues).
- On the frontend, TanStack caching and table virtualization prevented UI slowdowns on large datasets.
4) Test automation is the fastest way to ship safely
- Playwright E2E tests turned critical workflows into a deploy-time safety net.
- Sprint releases reduced blast radius and gave stakeholders frequent checkpoints.
- Feature-by-feature rollout lowered regression risk and improved trust in releases.